These days, it seems like we’re hearing about a new financial technology every other day. One of the most exciting new technologies to emerge is decentralized finance (DeFi). What exactly is DeFi? Decentralized finance (DeFi) is an emerging financial technology based on secure distributed ledgers similar to those used by cryptocurrencies. The system removes the need for a centralized bank, and provides a means for anyone to make or receive payments in any currency they choose. A blog article explaining what decentralized finance is and how it works.
Introduction
Decentralized finance—often called DeFi—refers to the shift from traditional, centralized financial systems to peer-to-peer finance enabled by decentralized technologies built on the Ethereum and other smart contract.DeFi has no centralised gatekeepers who can prevent access or reject payments, hence the markets are always open.DeFi proponents contend that services that were formerly expensive, slow, arbitrarily restricted, and arbitrary are now automatic and safer since they are handled by code that anybody can examine and scrutinise.
Decentralized finance has emerged as the most active industry in the blockchain world, with a variety of use cases for people, developers, and institutions, with over $54.56 billion in value now locked in defi through smart contracts.
In this blog post, we’ll give an overview of the DeFi ecosystem and some of the most popular protocols and applications in the space. We’ll also touch on some of the risks associated with investing in decentralized finance protocols and highlight some of the steps you can take to mitigate those risks.
Before beginning with DEFI, you should be familiar with smart contracts.
What Exactly Are Smart Contracts, and Why Should I Care?
A smart contract is an autonomous, self-executing contract that runs without the need for a central authority or rent-seeking third party in a decentralised, mathematically based world like a blockchain.Smart contracts maintain transparency and visibility on the blockchain by removing pointless paperwork and expensive middlemen needed to enable conventional contracts, transactions, and exchanges. They operate by generating a digital agreement or contract in which each side enters a number of predetermined requirements or clauses that must be fulfilled before the transaction can be implemented, directly and without the use of a middleman.
The real value of smart contracts comes from their diverse use cases, including payments (in cryptocurrencies or fiat) and supply chains, or from more complex applications that span across decentralised finance (DeFi), such as lending protocol, stablecoins, derivatives, decentralised exchanges, insurances, random number generation, betting and gambling, digital asset transfers, and so on.
In a word, smart contracts make sure that both party A and party B are carrying out their obligations under the contract.
What Functions Do Smart Contracts Serve in DeFi?
As the DeFi industry has grown from a modest sector in 2017 to one of the fastest growing sectors in the emerging technological landscape in 2022, the use of smart contracts has skyrocketed.Users of centralised financial institutions, like banks and credit unions, can rely on intermediaries to manage transactions, but DApps must use smart contracts to make sure that every transaction is legitimate, transparent, and trustless — and that the agreed-upon goods or services are actually being transferred.
What does TVL (total value locked) mean DeFi?
The overall value of crypto assets placed in a decentralised finance (DeFi) protocol, or in DeFi protocols in general, is known as total value locked (TVL). It has become a crucial statistic for assessing interest in that specific area of the cryptocurrency market. TVL incorporates all coins put in all of the DeFi protocols’ available services, such as: 1.Staking 2.Lending 3.Liquidity pools
The yield that these deposits are anticipated to receive is important to note. It only refers to the deposits’ actual present worth.
The TVL of a project might also vary as a result of user withdrawals or fresh deposits. Along with the fluctuating dollar worth of all those assets in the cryptocurrency market, it is always altering.
What is DeFi?
Decentralized applications (Dapps) offering financial services on a blockchain settlement layer, including as payments, lending, trading, investing, insurance, and asset management are together referred to as “DeFi.” DeFi services often function without centralised organisations or intermediaries and make use of open protocols that enable flexible programmatic service combining.
In the past, intermediaries have been crucial players in the financial markets, acting as agents and brokers of security, settlement, liquidity, and confidence. To fulfil the demands of an increasingly complex financial system, the variety and value of intermediaries have expanded over time.
DeFi uses blockchain technology to enable substitutes for established service providers and market frameworks. Building on current research in financial technology (fintech) and blockchain technology more broadly, it offers the possibility for innovation and the development of new services to increase the efficiency of financial markets.
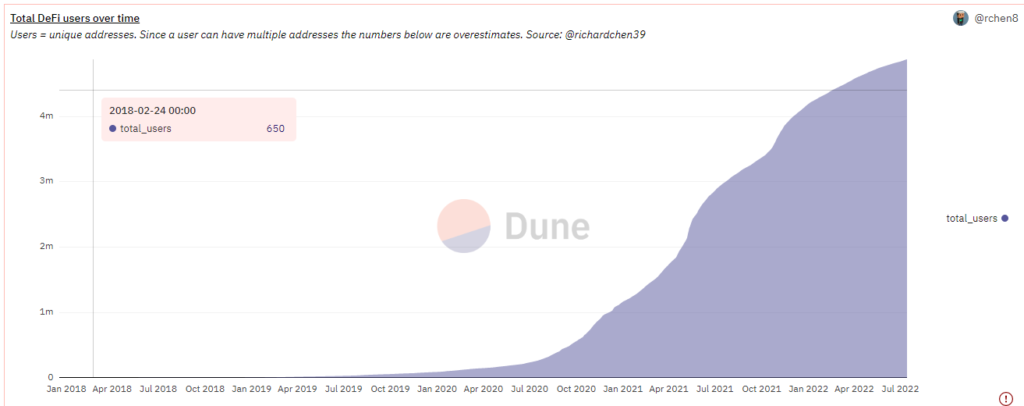
There were more over 480000 active DFI users as of September 2022.Users = unique addresses. Since a user can have multiple addresses the numbers below are overestimates. Source
DeFi infrastructure ecosystem
Blockchains:Distributed ledgers acting as the transaction settlement layer. Due to its features and developer acceptance, the majority of DeFi services currently run on the Ethereum network.
Digital Assets:Tokens that can be exchanged or transferred within a blockchain network. The first digital assets based on a blockchain were bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Others are designed to serve a variety of purposes other than payments.
Digital assets examples – Crypto assets,Stablecoins,Non-fungible tokens (NFTs),Security tokens,Domain.
Wallets:Software interfaces that let people control the assets kept on a blockchain. Through their private keys, users of non-custodial wallets have complete control over their money. Private keys for custodial wallets are controlled by a service provider.
Decentralized Applications (Dapps):Smart contract-based software applications are frequently integrated with conventional web technology’s user-facing interfaces.
Governance Systems:software-based systems that control changes to blockchain protocols or smart contracts, frequently based on tokens that grant stakeholders voting rights.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs):Entities whose laws are written and upheld using smart contracts.
Stablecoins:digital assets with values linked to a fiat currency, a group of fiat currencies, or other assets with a steady value.
Oracles:DeFi services can be combined with data feeds that provide information from sources outside of the blockchain, such as the current price of a stock or a fiat currency.
Key Features of Decentralized Finance
Decentralized:DeFi protocols are not regulated by central entities, like as banks and financial institutions, because they are built on decentralised blockchains like Ethereum avalanche. Instead, they are upheld by network users and developers.
Permissionless:There are no boundaries with DeFi, and anyone with a digital wallet and Internet access is welcome to use the protocols. There is no need for verification or registration.
Immutable:The code of a smart contract for any DeFi protocol is permanent and cannot be changed once it has been written.
Transparent:DeFi uses fully transparent blockchain technology to conduct its business. Anyone at any point may audit the code that is written in the smart contract.
Non-Custodial:DeFi gives customers complete control over their own data and assets because they are the ones who control their own digital wallets. Noncustodial refers to the fact that the user’s assets are not in the possession of any third parties.
Traditional Finance and DeFi Comparison
| Traditional Finance | DeFi |
| On behalf of asset owners, a regulated service provider or custodian holds the asset. | Held directly by users in non-custodial wallets or through escrow powered by smart contracts. |
| usually denominated in fiat money. | backed by digital assets or stablecoins, which may be itself backed by fiat currency. |
| Usually, intermediaries handle business dealings between parties. | using smart contracts that utilise the resources of the user. |
| processed, usually after a certain amount of time, by service providers or clearinghouses. | Writing transactions to the underlying blockchain completes the settlement process. |
| Rules established by the service provider, the market, the regulator, and/or a self-regulatory body specify this. | Auditors can validate protocols and activity thanks to open-source code and public ledgers. |
| authorised third-party examinations of proprietary code or possibilities for publicly verifiable open-source code | Overcollateralization is typically necessary because of the volatility of digital assets and the lack of credit scoring. |
| Transactions may entail no collateral, collateral that is equal to or less than the amount offered, or both. | On the same blockchain and maybe different chains, any service may integrate with any other service. |
| Service providers do identity checks. National privacy regulations apply to personal data. | Anti-money laundering regulators are debating identity verification measures. Balances held by users and recent transactions are generally open. |
| prone to data breaches and hackers in software systems in charge of assets. | vulnerable to hacking attempts and other smart contract operational and technical hazards. |
| government-mandated consumer protections, anti-fraud enforcement, exposure restrictions, and disclosure requirements insurance plans. | Users by default incur all risks, despite the fact that private redress options like DeFi insurance provide some loss protection. |
What Can DeFi Apps Do?
The term “DeFi” refers to a variety of acts that fit under the categories of open, composable, non-custodial, and trust-minimized financial services. DeFi apps are advancing in the following areas, to name a few.
Wallet
A DeFi wallet is a non-custodial wallet where you can save your bitcoin holdings. Being non-custodial, they are inaccessible to anybody without the secret key or seed phrase, which functions as a password. Governments can’t, for example, freeze the account, but they might be able to tell the token issuer to freeze assets transmitted to exchanges or make some assets useless.
1.Metamask 2. Go to Metamask 3. XDEFI 4. Go to XDEFI 5. Coin98 6. Go to Coin98 7. Frame 8. Go to Frame 9. Phantom 10. Go to Phantom 11. Solflare 12. Go to Solflare 13. Terra Staon 14. Go to Terra Staon 15. Keplr
Stablecoins
Stablecoins are essential to DeFi because they isolate the services’ risk/return calculations from the sometimes significant volatility of digital assets. Investors anticipate a constant unit of account for financial services, and financial interoperability necessitates stable pricing for value exchange.Stablecoins can be broadly divided into three groups. 1.Custodial 2.Asset-backed 3.Algorithmic
1.Tether 2.USD Coin 3.Binance USD 4.DAI 5.Gemini Dollar
Exchanges
In contrast, DeFi exchanges decentralise essential operations. Noncustodial wallets enable programmatic access to them. Smart contracts automatically handle transactions between peers or against a pool of money.
1.Uniswap 2. Sushiswap 3. Curve 4. Trader Joe 5. Pangolin 6. SpookySwap 7. SpiritSwap 8. Ref Trisolaris 9. Quickswap 10. dfyn 11. Dinoswap 12. Rubicon 13. Balancer 14. Raydium 15. Orca 16. Saber 17. Saros 18. Astroport 19. Terroswop 20. Loop Finance 21. Osmosis 22. Juno
Borrowing
Users can borrow a cryptocurrency asset using DeFi borrowing if they pledge another cryptocurrency as collateral. Smart contracts make it possible for features like immediately seizing the collateral in the event of a default by the borrower.
1.AAVE 2. Anchor Protocl 3. Apricot 4. Benqi 5. Blizz Finance 6. Compound 7. Cream 8. dForce 9. Geist 10. Hundred Finance 11. MarkerDAO 12. Mars Protocol 13. Oroin Money 14. Parrot 15. QiDAO 16. Solend 17. Tarot 18. umee 19. Vesta 20. Wepiggy 21. Xtoken
Insurance
A new form of DeFi insurer lets its clients pool and share risk before deciding on the legitimacy of individual claims. Smart contracts are used to record and enforce the decisions made by the group’s members.
1.Nexus 2.mutual Tidal
Yield farming
By leasing their crypto to the blockchain, a process known as staking, or by lending it to a borrower, cryptocurrency owners can generate an investment return.
1.Convex 2. Snowball 3. Penguin Finance 4. yieldyak 5. Liquid Driver 6. Reaper Farm 7. Adamant 8. Beefy 9. Pickle 10. Tulip 11. Francium 12. Apricot 13. Sunny Aggregator 14. ApolloDAO 15. Spectrum Protocol 16. Nexus Protocol
Dex Aggregator
A cryptocurrency exchange known as a decentralised exchange (DEX) runs independently of a central organisation or outside entity. As a result, users have complete control over the money they store or trade on DEXs, which are more secure than centralised exchanges. On the Ethereum blockchain, decentralised exchanges run, and they need Ethereum smart contracts to function. Centralized exchanges, on the other hand, are managed by a third party that takes money from trades.
1.CowSwap 2. 1inch 3. Paraswap 4. marker.io 5. Paraswap 6. Open Ocean 7. Zoocoin 8. Firebird 9. Slingshot 10. Matcha 11. Jupiter
Asset management
Based on risk tolerance, time horizons, diversity, and other factors, it aims to optimise the value of an asset portfolio.
1.Babylon Finance 2. dHEDGE 3. Index Coop 4. Enso 5. Aelin 6. Solrise 7. Investin 8. Symmetry 9. Nbula Protocal
Bridges
A cryptocurrency bridge is a programme that enables users to move their cryptocurrency between blockchain systems. Basically, there are no interpreters because each blockchain has its own language. Bridges were developed to address this issue, enabling users to transmit their cryptocurrency to other blockchains by minting tokens that reflect their cryptocurrency on the other blockchain and holding the tokens from the first blockchain.
1. Hop Synapse 2. Wormhole 3. Rainbow 4. SimpleSwap 5. Connext 6. Allbridge
Conclusion
Decentralized finance is a new way of handling financial transactions that is powered by blockchain technology. This means that it is not controlled by any central authority, but instead runs on a decentralized network of computers. This makes it much more secure and efficient than traditional financial systems. Decentralized finance has the potential to revolutionize the way we handle money, and it is already starting to gain traction in the mainstream world.
Sources
1.https://wifpr.wharton.upenn.edu/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/DeFi-Beyond-the-Hype.pdf
2.www.defillama.com
3.

Naren is a finance graduate who is passionate about cryptocurrency and blockchain technology. He demonstrates his expertise in these subjects by writing for cryptoetf.in. Thanks to his finance background, he is able to write effectively about cryptocurrency.
